Health Tips
Pneumonia
|
Pneumonia |
|
|
|
|
|
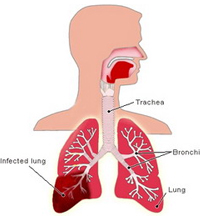
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can make you very sick. You may cough, run a fever, and have a hard time breathing. For most people, pneumonia can be treated at home. It often clears up in 2 to 3 weeks. But older adults, babies, and people with other diseases can become very ill. They may need to be in the hospital. |
 |
|
You can get pneumonia in your daily life, such as at school or work. This is called community-associated pneumonia. You can also get it when you are in a hospital or nursing home. This is called healthcare-associated pneumonia. It may be more severe because you already are ill. This topic focuses on pneumonia you get in your daily life. |
|
| Pneumonia usually starts when you breathe the germs into your lungs. You may be more likely to get the disease after having a cold or the flu. These illnesses make it hard for your lungs to fight infection, so it is easier to get pneumonia. Having a long-term, or chronic, disease like asthma, heart disease, cancer, or diabetes also makes you more likely to get pneumonia | |
|
What are the symptoms? |
|
| Symptoms of pneumonia caused by bacteria usually come on quickly. They may include: • Cough. You will likely cough up mucus (sputum) from your lungs. Mucus may be rusty or green or tinged with blood. Fever. • Fast breathing and feeling short of breath. • Shaking and "teeth-chattering" chills. You may have this only one time or many times. • Chest pain that often feels worse when you cough or breathe in. • Fast heartbeat. • Feeling very tired or feeling very weak. • Nausea and vomiting. • Diarrhea. |
 |
| Preventing pneumonia | |
|
1. Health care to be healthy and exercise regularly |
|